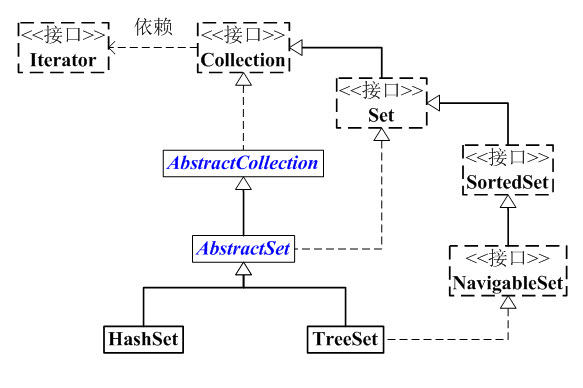
Set的核心概念就是集合内所有元素不重复。在Set这个子接口中没有在Collection特别实现什么额外的方法,应该只是定义了一个Set概念。
(01) Set 是继承于Collection的接口。它是一个不允许有重复元素的集合。
(02) AbstractSet 是一个抽象类,它继承于AbstractCollection,AbstractCollection实现了Set中的绝大部分函数,为Set的实现类提供了便利。
(03) HastSet 和 TreeSet 是Set的两个实现类。
HashSet依赖于HashMap,它实际上是通过HashMap实现的。HashSet中的元素是无序的。
TreeSet依赖于TreeMap,它实际上是通过TreeMap实现的。TreeSet中的元素是有序的。
| Set实现 | 使用场景 | 数据结构 |
|---|---|---|
| HashSet | 无序的、无重复的数据集合 | 基于HashMap |
| LinkedSet | 维护次序的HashSet | 基于LinkedHashMap |
| TreeSet | 保持元素大小次序的集合,元素需要实现Comparable接口 | 基于TreeMap |
| 常用方法 |
|---|
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| add() | add( )Adds an object to the collection. |
| clear() | clear( )Removes all objects from the collection. |
| contain() | contains( )Returns true if a specified object is an element within the collection. |
| isEmpty() | isEmpty( )Returns true if the collection has no elements. |
| iterator() | iterator( )Returns an Iterator object for the collection, which may be used to retrieve an object. |
| remove() | remove( )Removes a specified object from the collection. |
| size() | size( )Returns the number of elements in the collection. |
一个例子:
import java.util.*;
public class SetDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int count[] = {34, 22,10,60,30,22};
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
try {
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
set.add(count[i]);
}
System.out.println(set);
TreeSet sortedSet = new TreeSet<Integer>(set);
System.out.println("The sorted list is:");
System.out.println(sortedSet);
System.out.println("The First element of the set is: "+ (Integer)sortedSet.first());
System.out.println("The last element of the set is: "+ (Integer)sortedSet.last());
}
catch(Exception e) {}
}
}
hashcode()和equals()
http://www.oschina.net/question/82993\_75533
hashcode()计算对象的哈希值(一定要正确地重写,要不然错误很多),如果两个对象的hashcode()返回值一样,在set中算重复
equals()判断两个对象是否相等